Regulation of Diacylglycerol Content in Olfactory Neurons Determines Forgetting or Retrieval of Olfactory Memory in Caenorhabditis elegans

Behavioral Forgetting of Olfactory Learning Is Mediated by Interneuron- Regulated Network Plasticity in Caenorhabditis elegans

A behavioral switch: cGMP and PKC signaling in olfactory neurons reverses odor preference in C. elegans. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Forgetting of Adaptation to Diacetyl Is Regulated through a TIR-1/JNK-1

Proper DAG signaling is important for control of forgetting. Two

Caenorhabditis elegans Olfaction Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Neuroscience

Multiple Memory Traces for Olfactory Reward Learning in Drosophila

Dose-dependent suppression of LTM a–c, Conditioned wild-type (Canton-S)
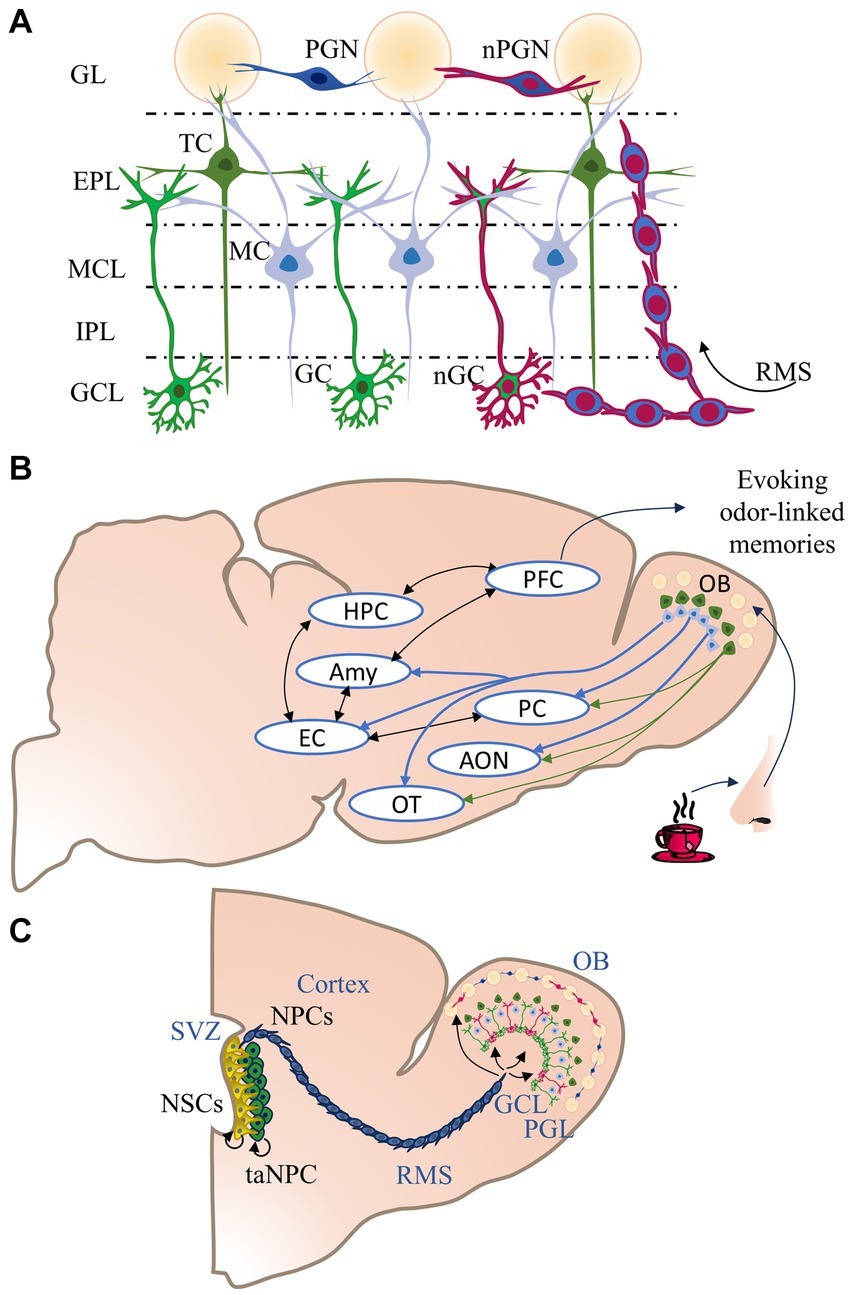
Frontiers Olfactory neurogenesis and its role in fear memory modulation

Illuminating neural circuits and behaviour in Caenorhabditis elegans with optogenetics

Behavioral Forgetting of Olfactory Learning Is Mediated by Interneuron- Regulated Network Plasticity in Caenorhabditis elegans

Goalpha regulates olfactory adaptation by antagonizing Gqalpha-DAG signaling in Caenorhabditis elegans. - Abstract - Europe PMC

Forgetting of Adaptation to Diacetyl Is Regulated through a TIR-1/JNK-1

A behavioral switch: cGMP and PKC signaling in olfactory neurons reverses odor preference in C. elegans. - Abstract - Europe PMC

EGL‐4/PKG regulates the role of an interneuron in a chemotaxis circuit of C. elegans through mediating integration of sensory signals - Hino - 2021 - Genes to Cells - Wiley Online Library

Molecular encoding and synaptic decoding of context during salt chemotaxis in C. elegans









