Determining the Role of Maternally-Expressed Genes in Early Development with Maternal Crispants

Rapid generation of maternal mutants via oocyte transgenic expression of CRISPR-Cas9 and sgRNAs in zebrafish

Early zebrafish development: it's in the maternal genes.

PDF] Mechanisms of maternal mRNA regulation: implications for mammalian early embryonic development.
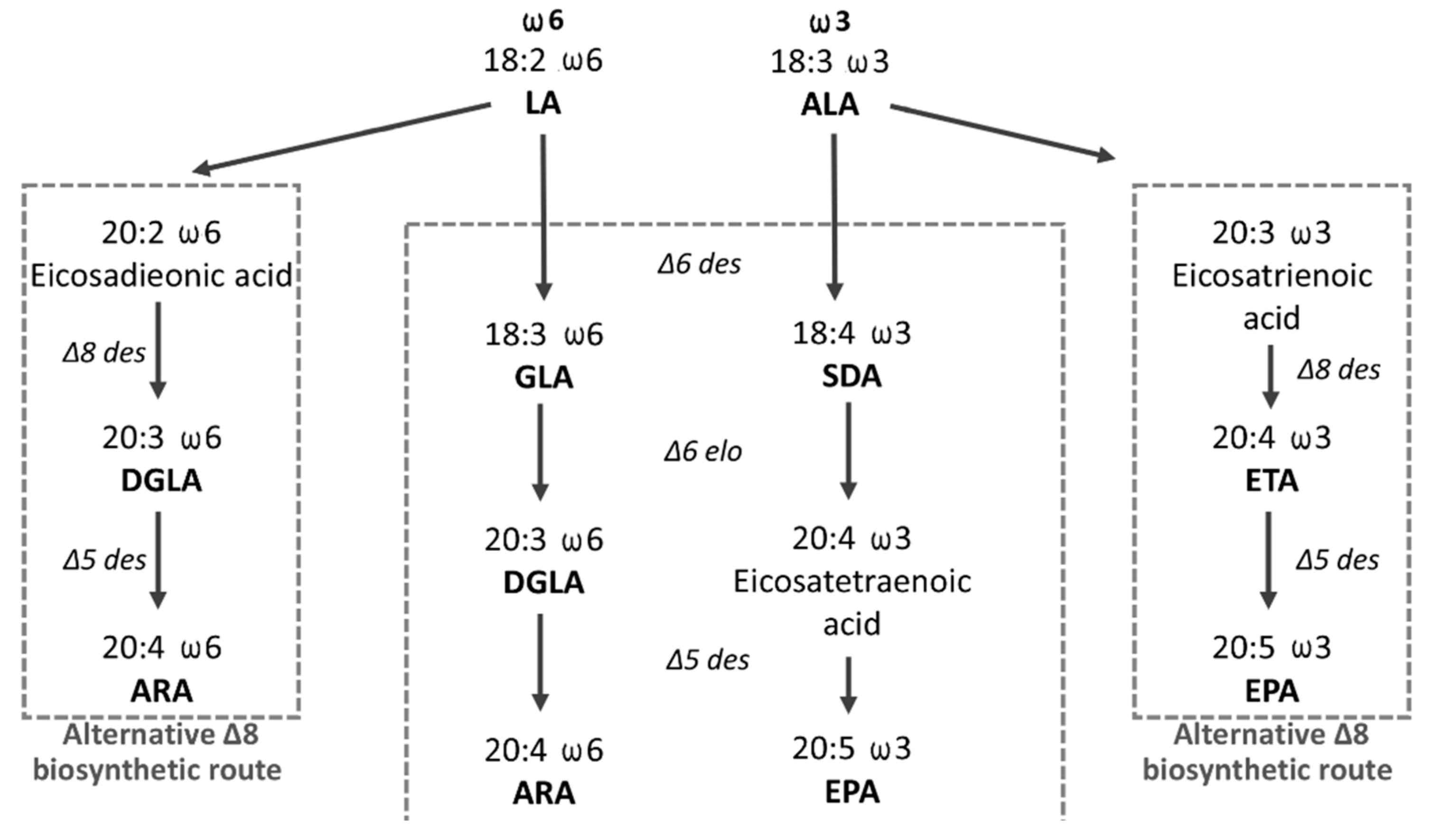
Genes, Free Full-Text

Loss of Fgf-responsive Pea3 transcription factors results in ciliopathy-associated phenotypes during early zebrafish development

Identification of Maternal-Effect Genes in Zebrafish using Maternal Crispants

Mutation of Kpna7 caused reproductivity reduction and sex imbalance. A

KPNA7 is vital for the maintenance of proper nuclear morphology. a

Maternal immune activation alters placental histone-3 lysine-9 tri-methylation, offspring sensorimotor processing, and hypothalamic transposable element expression in a sex-specific manner - ScienceDirect

HOX epimutations driven by maternal SMCHD1/LRIF1 haploinsufficiency trigger homeotic transformations in genetically wildtype offspring

Germline deletion of dgcr8 disrupts canonical microRNA function. a

motley is a mutation in birc5b, which causes early cell division




/s3.amazonaws.com/arc-authors/ipmgroup/dbef88af-a777-4e76-9966-40b1fd6e9729.png)




