Geologists shed light on the Tibetan Plateau origin puzzle: an
Earth's geographical surfaces formed over millions of years, and various theories aim to explain their formation. The most popular theory, called plate tectonics, states that Earth's outermost layer is a dynamic system consisting of slowly moving plates, also known as tectonic plates. As theses plates move, they come close to each other and collide, or drift away from or slide past each other, causing tension or rupture along their boundaries. During the enormous compression force along the rupture line of two plates, a slab of the earth can uplift. The uplifted piece of land gives rise to geographical structures such as mountains or plateaus on the landscape of the earth.

A) Tectonic map of the Tibetan Plateau. (B) Simplified map showing

Geological riddle solved: 'Roof of the World' has gotten higher

The formation and evolution of Africa from the Archaean to Present: introduction

Tectonic framework of the Tibetan Plateau and Himalayas (Zhu

Dynamics of the Earth's Surface in the Eastern Tibetan Plateau - Eos

Carboniferous-Permian sequences of the western margin of Sibumasu Block: Implications for new lithostratigraphic correlation in the eastern Highlands of Myanmar - ScienceDirect

Carboniferous-Permian sequences of the western margin of Sibumasu Block: Implications for new lithostratigraphic correlation in the eastern Highlands of Myanmar - ScienceDirect

Main tectonic entities and distribution of eclogite in the interior of

Tibetan Plateau - Wikipedia

PDF) Tibetan Plateau: An evolutionary junction for the history of modern biodiversity

Archaeologists Shed More Light on Colonization of Tibetan Plateau

Geological Marvels - FasterCapital
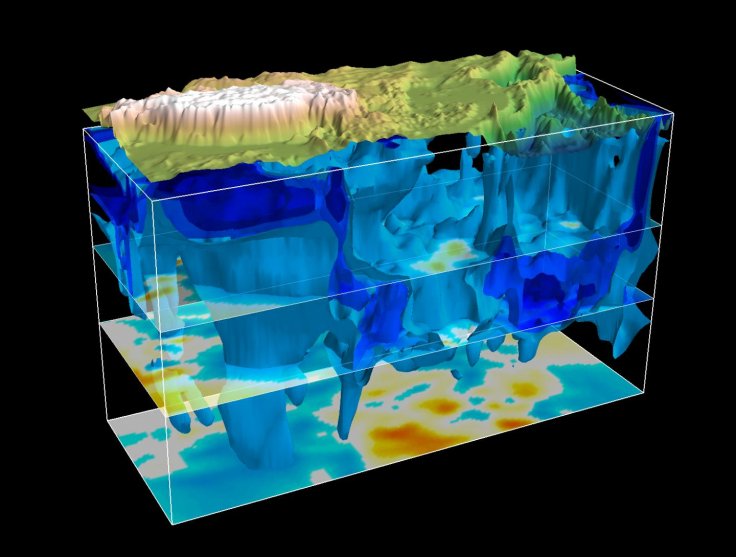
Massive, fast moving structure seen beneath Tibetan Plateau in earthquake simulation study

Tales set in stone: 40 years of the International Geoscience Programme (IGCP)









